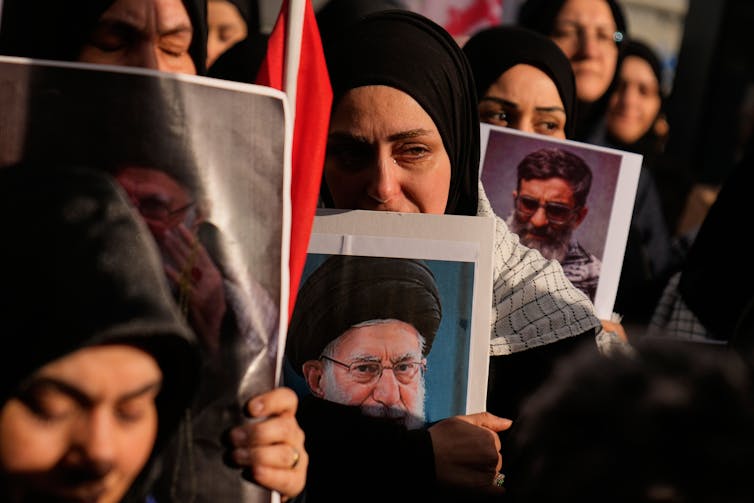
The day Ayatollah Ali Khamenei was killed, the Iranian government called for 40 days of public mourning in line with Shiite tradition. It also praised the supreme leader for his martyrdom – a concept considered sacred and significant in the Islamic Republic and Shiite Islam.
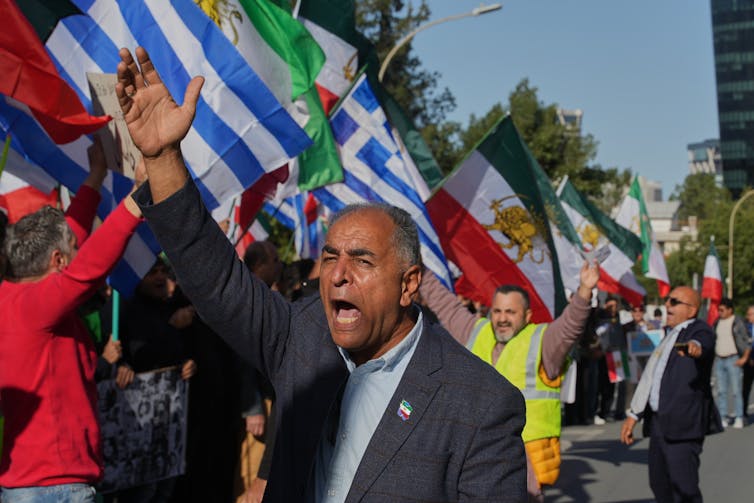
While some Iranians came out to commemorate Khamenei, others celebrated his demise. The scenes reflected the contradictions in how Khamenei was perceived: by some as a martyr, and by others as an oppressor.
The theology of martyrdom
The roots of Shiite reverence for martyrdom date back centuries. After the death of the Prophet Muhammad in 632, a dispute emerged over who would inherit the leadership of the Muslim community. On one side was the prophet’s senior companion and father-in-law, Abu Bakr. On the other was his cousin and son-in-law, Ali ibn Abi Talib, who became the first Shiite imam.
In 680, the Battle of Karbala took place in present-day Iraq between Hussain ibn Ali – the grandson of the Prophet Muhammad and the third Shiite imam – and Yazid ibn Mu'awiya. Yazid was the second Umayyad caliph, which means deputy of God, and the ruler of the early Islamic empire.
Before the battle, negotiations had failed between Hussain and Yazid’s governor. Hussain refused to swear allegiance to Yazid, believing him to be unjust and not the rightful successor. In a 10-day battle that followed, most of Hussain’s army, including some of his closest companions and relatives, was slain. Hussain’s followers, who believed him to be the third Imam – after his father Ali and older brother Hasan ibn Ali – came to be called Shiites. Since then, martyrdom has held a central place among Shiites. They comprise the smaller of the two main branches of Islam, with Sunni being the larger one.
Iran has become the epicenter of Shiite Islam, which is the official state religion. Ninety to 95% of the population identify accordingly.
Every year on the 10th of Muharram, the first month of the Islamic calendar and the same day as the Battle of Karbala, Shiite Muslims inside and outside of Iran observe Ashura and commemorate the slaying of Hussain by reenacting his death and performing self-flagellation, among other rituals.
Iranian political rhetoric
In Iran and other parts of the Muslim world, contemporary politics is often framed in this seventh-century language of moral resistance.
After the Islamic Republic of Iran was established under Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini in 1979, martyrdom appeared as a central theme. This was particularly the case during and after the Iran-Iraq War, which lasted eight years in the 1980s and was perceived and portrayed as a holy war.
During the war, the Islamic Republic suffered hundreds of thousands of casualties. After Khomeini reluctantly accepted a United Nations-brokered ceasefire, he compared the decision to drinking a “poisoned chalice.” In other words, he considered the compromise a crushing defeat that contradicted his goal of overthrowing Iraqi President Saddam Hussein, even if it enabled the Iranian regime to survive.
After the war, public space in Iran was increasingly filled with revolutionary and religious symbols related to wartime sacrifice and martyrdom. They included street signs named after prominent people who died in the war, murals and posters of the fallen, and media programs and publications dedicated to the conflict – symbols which were still prominent when I visited Iran between 2009-2011.
The Islamic Republic’s Foundation of Martyrs and Veterans Affairs – Bonyad-e Shahid va Omur-e Ithargaran – provided services for veterans and families of the fallen in the war and other conflicts. Like other foundations under the purview of Khamenei, who succeeded Khomeini after his death in 1989, it also participated in profit-seeking activities.
It is against this backdrop that Khamenei’s actions leading up to the American and Israeli strikes on Feb. 28 that cost him his life must be seen.
During the three rounds of U.S.-Iran negotiations in Oman and Geneva before the current conflict, Khamenei refused to capitulate to President Donald Trump’s demands. They comprised curbing not only Iran’s nuclear enrichment, but also its missile program and support for its regional proxies. Khamenei directed his negotiators not to yield ground, particularly on those last two points, seen as red lines in Tehran – even as Trump amassed the most military assets in the region since the U.S. invasion of Iraq in 2003.
Authoritarianism, protests, polarization
For over three decades, Khamenei subjected Iranians to severe authoritarianism and repression, culminating in him ordering the security forces to shoot and kill thousands of Iranians during the protests in January 2026, not to mention those in previous years.
He deprived the families of deceased protesters from holding funerals for their loved ones. His regime also reportedly required them to pay for the ammunition that had been used to kill their relatives before receiving the body for burial.
And despite recurrent waves of protests – the January unrest followed similar waves in 2017-18, 2019-20 and 2022-23 – Khamenei refused to listen to the demands of demonstrators for political, economic and social change. The furthest he was willing to go was to make cosmetic concessions while ruthlessly repressing citizens.
He also refused to reform the system from within and placed the political elites who pushed him in that direction under house arrest or in prison.
During his almost 37-year rule, Khamenei accumulated massive power and wealth. As supreme leader, he commanded the armed forces, appointed the head of the judiciary, supervised the state media, and possessed a parallel body that vetted electoral candidates and vetoed parliamentary legislation.
Although Khamenei appeared austere in public, he held sizeable assets. Setad, a quasi-state organization under his direct control, was estimated to be worth US$95 billion as of 2013.
He continued support for regional proxies, such as Hamas and Hezbollah, while maintaining a confrontational rhetoric toward the U.S. and Israel. Since 2024, these actions led to Israeli and American intervention in Iran that brought death and destruction to the country, and ultimately the strikes that killed him. The strikes also killed some of his closest relatives, including his daughter, son-in-law, grandchild and daughter-in-law.
In the end, some Iranians will remember Khamenei as a martyr – someone who stood firmly by his principles and faced a more powerful enemy, even if it meant losing his life.
Eric Lob, Associate Professor of Politics and International Relations, Florida International University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.






 The Joy of Driving, Reimagined
The Joy of Driving, Reimagined